About Us
Why choose us?

- We are a Dental Clinic founded by three sisters, professionals in different specialties. They are in charge of making you feel at home at Dental Solutions, here you will have an amazing treatment you won’t find in any other clinic in Los Algodones: friendly, sensitive, professional, and homely
- You will save up to 80% in your treatments over USA and Canada prices
- We are committed to offer you a personalized and integral attention to help you protect and regain your smile, your confidence and self-esteem with effective and affordable treatments
- Our staff is highly trained and is constantly attending courses, certifications, specialties and seminars in several prestigious institutions such as Harvard Medical School, Malo Institute in Portugal and Megagen Implants in South Korea
- We are members of the ADA (American Dental Association)
- We work with the most advanced CAD/CAM technologies to design and manufacture our dental implants, with the same quality and materials (Nobel Biocare and 3i) used by any US clinic
- You can pay using credit cards, debit cards, personal checks and cash
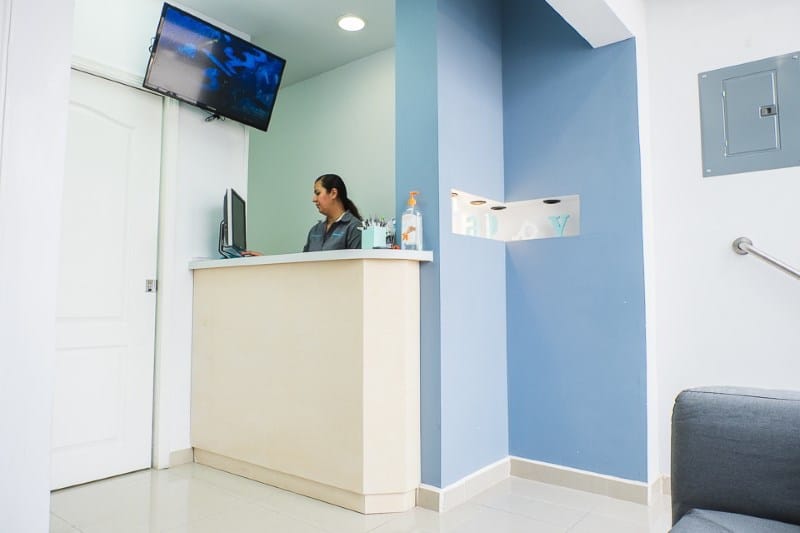
- You will enjoy your waiting at a comfortable lobby with WiFi, access to telephone calls to US and Canada and an LCD TV
- Our prices are public, without hidden fees or surprises. You can check them here
- Our staff has more than 8 years of experience attending Canada and US patients
- We are specialists in the All-on-4 treatment. More than 1,200 successful All-on-4 implant
Still not convinced? Read some of the reviews that some of our clients have written us.
Already convinced? Click here to schedule your appointment today! And get an exclusive 4% discount on any of our treatments or a 500 USD discount in the full mouth all-on-4.
GET A FREE ESTIMATE: